Liver Cancer
What is liver cancer?
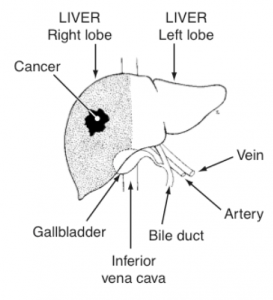
The functions of the liver include filtering out harmful substances in blood, storing nutrients, converting fats to energy, and helping the blood to clot. Liver cancer occurs when cells in the liver become malignant, or cancerous.
The two types of cancerous liver tumours are primary and metastatic(also called secondary):
- Primary cancers, which are less common in Western countries, begin in the liver. Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common type. People with cirrhosis of the liver, or those who have been infected with a hepatitis virus have a higher risk of getting primary liver cancer.
- Metastatic liver cancer is much more common than primary liver cancer in Australia and occurs when cancer cells carried in the blood from other gastrointestinal organs, like the colon or stomach, become lodged in the liver and become tumourous. These cancer cells can also be spread in the lymphatic system.
What are the signs and symptoms of liver cancer?
The signs and symptoms of bile duct cancer may include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Upper right quadrant abdominal pain
- Jaundice
- Weight loss
- Abdominal distension
Which test(s) and/or procedure(s) may be requested to determine if I have liver cancer?
Tests and procedures that can help detect liver cancer include blood test, ultrasound, CT scan, and MRI scan.
Video Link for Liver Cancer
How is this condition surgically treated?
It can be difficult to operate on the liver because of its position near major blood vessels and the rib cage and the fact that it is large, dense and delicate. Treatment depends on whether the cancer is localised and operable, if it has spread through the liver and other parts of the body and if it has returned after an initial treatment. The most common surgical treatments for liver cancer are liver resection and liver transplantation. A liver transplant may only be considered if a patient has another liver disease, like cirrhosis, and also depends on the extent of the cancer.
Image guided procedures, for instance, may be performed through the skin without an incision to control the spread of cancer. These include:
- Radiofrequency ablation or Microwave ablation, where energy is used to destroy the cancer.
- Transarterial Chemoembolisation, where chemotherapy agent is injected directly via the tumour’s blood supply.
Video References
Liver Cancer
Radiofrequency Ablation Of Liver Tumours
Transarterial Chemoembolisation Of Liver Tumours
Norwest GI is here to help you
If you would like to find out more about any of the information above, or would like to book an appointment for a discussion,
please give the Norwest GI team a call today on 02 9899 7322 or complete our contact form and one of our friendly staff will be in touch shortly.